|
|
Lei Pan 潘磊 Master of Science & Engineering Computer application technology Image-Guided Surgery and Therapy Laboratory Email: lionpan@sjtu.edu.cn Laboratory: 5209 Software Building SJTU Phone: +86-21-34204391 Mailing: 5209 |
Biography
Lei Pan, came from Huizhou, which is a
beautiful (comfortable) seashore city in
Now he is doing research work at the Image-Guided Surgery and Therapy Laboratory (IGST), supervised by Prof. Lixu Gu. And he is now working as teaching assistant for the school and research assistant for the professors. He is always an active member in the campus. Lei participated in Student Council Organization of the school and led the group of study and research for bachelor students. He was the major member of the basketball team as a point guard for school of software engineering.
Research interests
His research interests include Computer Graphics, Biomechanics, Finite Element Method, Organ morphological analysis, 3DImage Segmentation, GPU algorithm and accelerating in image processing, Soft issue deformation modeling.
Education
Lei Pan finished his senior high school
study from 2001 to 2004 and junior from 1998 to 2001 at Huizhou No.1 Middle
School. Lei Pan studied in
Research
|
|
GPU-based image processing Large scale of 3D medical image data can be
efficiently processed by GPU based on its parallel computation capability.
From Cg and HLSL for old type GPU(Nvidia™ 6 Series) to CUDA for new type GPU(Nvidia™ 8 Series), GPU is a powerful tool and has been
widely used in my research work for segmentation and visualization. |
|
|
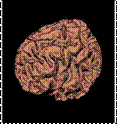
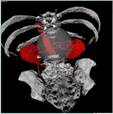
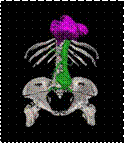
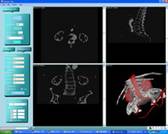
3D medical image segmentation Image Segmentation is part of my research work at
IGST laboratory. I was segmenting brain, abdomen, vertebra, aorta using kinds
of basic segmentation algorithms from September, 2006 to October, 2007. |
|
|
Organ Morphological analysis Morphological
analysis is the basic of human organs segmentation if using morphological
algorithm. Erosion, dilation and other methods can affect the final segmental
results. |
|
|
MIPS Visualization It is part of my segmentation work. MIPS is a visualization algorithm which supplies a specific
view and useful information of the 3D objects. It is comparatively
easy-implemented in GPU. |
|
|
Multi-Level immersing
Watershed Segmentation Watershed is a basic algorithm in segmentation.
However it always brings to an over-segmented result. Multi-Level immersing
watershed was proposed to reduce the region that is over-segmented. I was
doing my research on it and applied it to the brain from December, 2007 to
April, 2008. |
|
|
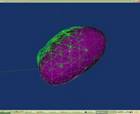
Deformation simulation in Finite Element Method Deformation model is my current major research work
at IGST laboratory. My deformation model is based on tetra mesh and finite
element method. It is mainly applied for simulating human soft issues and
organs when doctors are operating. |
|
|
Matrix solver on GPU FEM introduced large scale of matrix during
computing the displacement of each finite element. Matrix computation can be
accelerated by general purpose GPU. Implementing matrix solver on GPU is part
of my current work. |
|
|
Linear and Non-linear FEM Research on both
linear and non-linear fem deformation on common models. Comparison between
the deformed results. Analysis the boundary condition on non-linear
deformation model. |
|
|
Spine Operation Project Current project
in IGST cooperating with |
Publications
First Author:
Implementation of medical image segmentation in CUDA
Lei Pan; Lixu Gu; Jianrong
Xu
International Conference on Technology and
Applications in Biomedicine, 2008. (ITAB 2008).
30-31 May 2008 Page(s):82 - 85
Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ITAB.2008.4570542
Abstract
As the fast development of GPU, people tend
to use it for more general purposes than its original graphic related work. The
high parallel computation capabilities of GPU are welcomed by programmers who
work at medical image processing which always have to deal with a large scale
of voxel computation. The birth of NVIDIA® CUDA™
technology and CUDA-enabled GPUs brought a revolution
in the general purpose GPU area. In this paper, we propose the implementation
of several medical image segmentation algorithms using CUDA and CUDA-enabled GPUs, compare their performance and results to the previous
implementation in old version of GPU and CPU, indicate the advantages of using
CUDA technology and how to design algorithm to make full use of it.
An Improved Facial Orthopedic
Surgery Planning System with Pre-processing FEM Modeling
Lei
Pan, Lixu Gu,
Zhennan Yan, Sizhe Lv, Bo Zhu
18th
International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence
(ICAT08)
Abstract
Finite Element Method(FEM), which is based upon
continuum mechanics and the physics of materials, is one of the most widely
used deformation method in digital biomedical area. Unlike other light-weighted
deformation models (Mass-Spring, Free Form, Chainmail, BEM, etc)using in other areas, FEM gets the most accurate deforming
results in the cost of large scale of computation. In this paper, we present an
improved Facial Orthopedic Surgery Planning system using pre-processing FEM
modeling. This planning system calculates and simulates the bone-reshaped
surgical result of facial soft issue deformation more quickly. According to the
specific demands of the facial surgery planning system, we designed and
implemented FEM modeling in our own way and improved the computational
efficiency. Finally we validate and represent the deformation results, compare
our method and results with the traditional one.
Co-Author:
Simulation of organ deformation using boundary element
method and meshless shape matching
Bo
Zhu,; Lixu Gu,; Jingsi Zhang,; Zhennan Yan,; Lei
Pan,; Qiang Zhao,;
Engineering
in Medicine and Biology Society, 2008. EMBS 2008. 30th
Annual International Conference of the IEEE 20-25 Aug. 2008 Page(s):3253 -
3256
Abstract
In this paper, a novel approach to perform real-time simulation of
the deformation of anatomical organs is proposed for virtual surgery study. The
method, which is both physics and interactivity motivated, is composed of two
algorithms: boundary element method and meshless
shape matching. We employ boundary element method to simulate a precise global
deformation, and use meshless shape matching method
to achieve low latency. In addition, a state machine is applied to control the
computation patterns of deformation. The initial experiment reveals that the
proposed approach can simulate organ deformations both efficiently and
accurately.
Delaunay Mesh
Reconstruction From 3D Medical Images Based On Centroidal Voronoi Tessellations
Sizhe Lv, Xubo Yang, Lixu Gu,
Xiaojin Xing and Lei Pan
The International
Conference on Computational Intelligence and Software Engineering 2009 (CiSE 09)
Abstract
Reconstructing meshes from 3D medical images is an important but
complicated task, which provides a fundamental data structure for Bio-medical
applications. In this paper, a novel and easily implemental solution is
proposed. Instead of following the popular methods, we sample on the medical
images with centroidal Voronoi
tessellations, and then build the Delaunay mesh from the sampled points
directly. By applying the algorithm on the CT images and evaluating the mesh
quality metrics, the solution presents to be good at reconstructing complicated
objects and generates optimized meshes, which shows that it is suitable for
anatomical structure modeling.
A Saliency Constrained Multi-level Immersion Watershed transformation
for Medical Image Segmentation
Xiaopeng Peng,
Lixu Gu,
Lei Pan, Qionghua Weng
International Symposium on
Bioelectronics and Bioinformatics 2009 (ISBB 2009).
Abstract
Omitted
Working
|
|
Hitachi Image Group 2006-2008 |
|
|
Intel Software Center
Shanghai cooperates with School of Software, |
|
|
As a student of School of
Software Engineering, Lei Pan also works as Vice-Class
Representative, Vice-President of the
Study and Research Group of the School, Teaching
assistant of C++ Programming, Data structure and Algorithm Classes and
Teacher taking charge of frosh class. |
Artifacts
|
|
Level-Ace Online Bookstore deployed on distributed
database system Web application. Course Project in “Introduction of
Software engineering”. An Online bookstore system realized by J2SE and Flash
technology, designed in MVC pattern. Using JSP, servlets,
sessions, cookies, RMI, cloudscape and JAVA beans. |
|
|
Tortoise Drawing and Logo language Compiler Summer project in 2006. It is a Logo language
editor, compiler and tortoise drawer implemented by Microsoft MFC. It is
based on several advanced dialogs which handles the command of editing,
compiling, drawing and user interacting. It supports extern coding, result
export, embedded functions, recursions, skin changes, etc. |
|
Command line program |
Level-Set application in heart image An application of an existed level-set algorithm on
2D and 3D heart images. |
|
|
MIPS Visualization using GPU A visualization requirement from Hitachi Medical
Group. Using MIPS method to display 3D medical images and their segmentation
results. MIPS is implemented in GPU using HLSL to
compute the rotation of the images in parallel. It supports kinds of user
interaction |
|
|
DirectX 3D medical image Viewer and Reconstructor A complete system requirement from Hitachi Image
Group, |
|
Command line program |
Easy Java Compiler |
|
|
Stage light and shadow System Course project in “Computer Graphics”. It is a
system that simulates the stage light and shadow of the actors and other
objects. User can control the number, color and position of the lights around
the user defined stage and also the size, texture and moving action of the
actors. It is an application of several principles of Computer Graphics and
is implemented in OpenGL. |
|
|
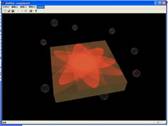
3D Snow simulation A small program that simulates large amounts of
moving objects in the scene implemented in Managed C++/DirectX and GPU. The
number of flakes is decided by the memory of GPU. It consider
the influence of the gravity, wind force, velocity, density and acceleration. |
Hobbies:
Basketball
Lei was major member of Grade team in High School and College team in
Sneaker
collection
Lei was influenced by the sneaker culture since he was in primary school. Lei owns a full series collection of Allen Iverson’s sneakers.
Music
Lei is familiar with and likes Cantonese Pop music very much. His favorites singer is Eason Chan.
Movie
Lei always watches movies on his spare time. He pays special attention to the digital vision effect, which is related to his research work (like object deformation), shown in the scene of the movie.
Last Update: September 2, 2009, Lei Pan, lionpan@sjtu.edu.cn
Copyright ©2006-2008 Lionpan, Image-Guided Surgery and Therapy Laboratory, School of Software Engineering, 5209 Software Building, Shanghai Jiaotong University, 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai, 200240, P.R.China.